Table of Contents
Introduction
Space is not just a vast, empty expanse; it’s a stage where celestial bodies dance to the tune of gravity. Within this cosmic ballet, there are special places where the forces of gravity reach an exquisite equilibrium, allowing objects to stay in a stable and seemingly magical formation. These points are known as Lagrange points, and they represent a fascinating aspect of celestial mechanics. In this blog post, we will delve into the concept of Lagrange points, their significance, and the role they play in space exploration and astronomy.
Understanding the Basics
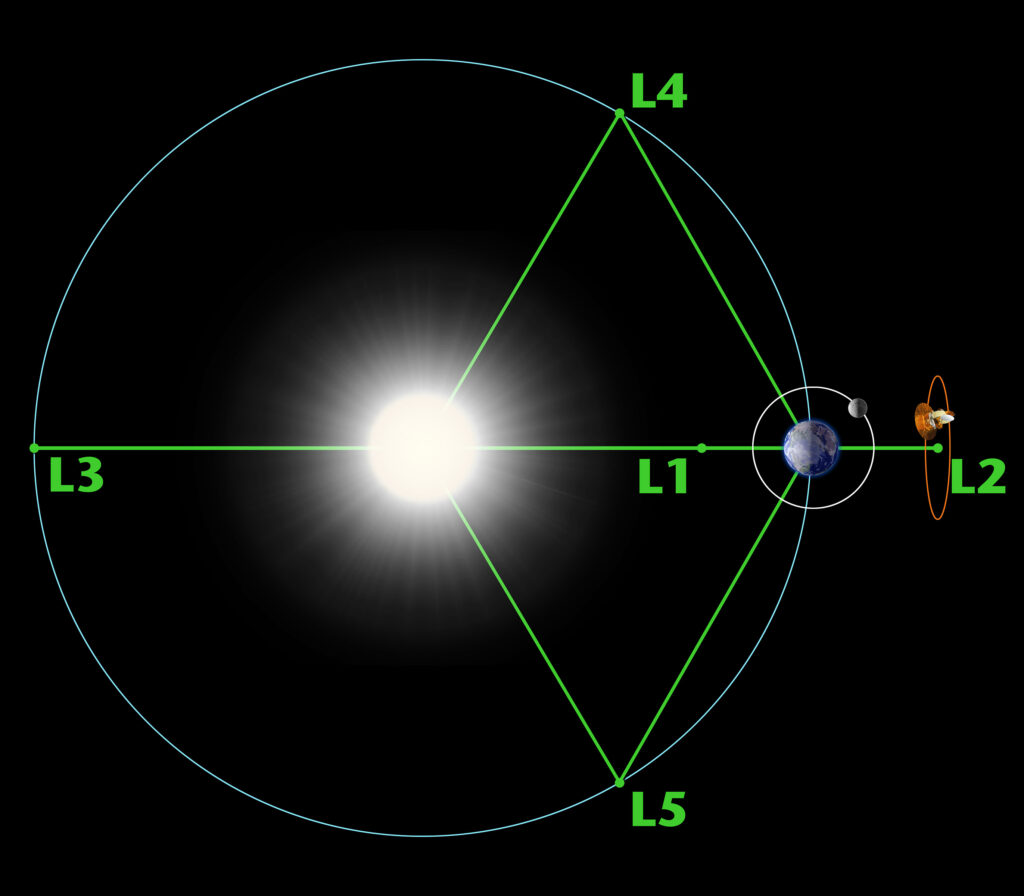
To comprehend Lagrange points, we first need to grasp the fundamental principles of gravitational attraction. Sir Isaac Newton’s law of universal gravitation tells us that every mass in the universe attracts every other mass. In the context of celestial bodies like planets, moons, and satellites, this gravitational attraction shapes their orbits. Lagrange points are the result of the interplay between gravitational forces from two massive bodies, typically a planet and a moon or a planet and the Sun. There are five Lagrange points in any two-body system, labeled L1 through L5. L1, L2, and L3 lie along the line connecting the two massive bodies, while L4 and L5 form an equilateral triangle with them.
Lagrange points : The Magic of Gravitational Balance
At Lagrange points, the gravitational forces of the two massive bodies balance perfectly. This equilibrium creates a stable point where a smaller object, like a spacecraft or a satellite, can remain fixed relative to the two larger bodies. Think of it as finding a cosmic sweet spot where the gravitational pulls from the planet and its moon (or the planet and the Sun) cancel each other out.
Applications in Space Exploration
Stable Orbits and Satellite Operations :- Lagrange points, particularly L1 and L2, are ideal locations for placing satellites and observatories. Here’s why:
Uninterrupted Views :- Satellites stationed at Lagrange points can maintain a relatively constant position relative to Earth or other celestial bodies. This stability ensures uninterrupted observations of specific regions of space or celestial objects, which is crucial for scientific research and long-term monitoring.
Reduced Fuel Consumption :- Unlike satellites in traditional geostationary orbits, those at Lagrange points require minimal station-keeping maneuvers to maintain their positions. This results in significant fuel savings and prolongs the operational lifespan of these satellites.
Observing Cosmic Phenomena :- Space telescopes like the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) are placed at L2 to observe distant galaxies, stars, and other celestial objects. By residing at this Lagrange point, the JWST can maintain a clear view of the cosmos without interference from Earth’s atmosphere.
Interplanetary Travel and Rendezvous :- Lagrange points are valuable for staging interplanetary missions and rendezvousing with celestial bodies:
Gravity-Assist Maneuvers :- Spacecraft can use Lagrange points as waypoints for gravity-assist maneuvers when traveling between planets. By leveraging the gravitational pull of these points, missions can conserve fuel and gain energy for their journeys.
Asteroid Exploration: Lagrange points can serve as ideal locations for spacecraft to rendezvous with and study asteroids. By hovering near these points, spacecraft can maintain a stable position relative to the target asteroid, enabling detailed observations and sample collection.
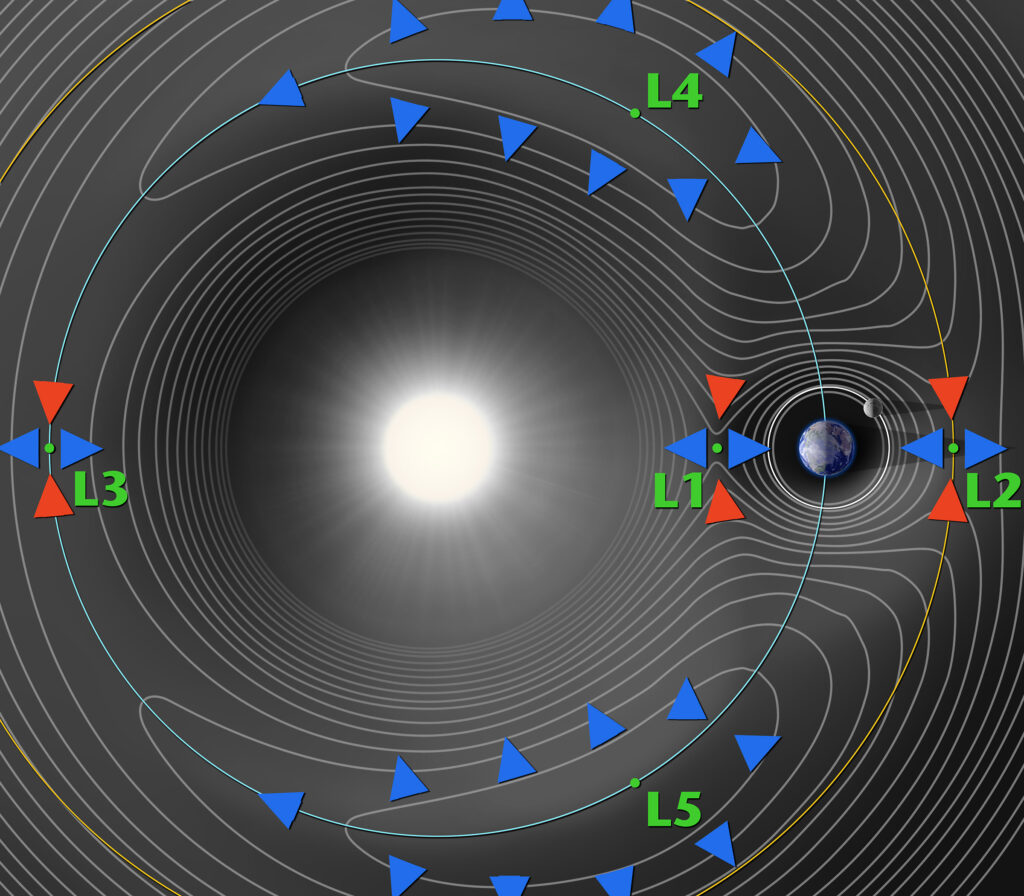
Solar and Space Weather Monitoring :-
L1 is a strategic location for observing the Sun and monitoring space weather:
Solar Observatories :- Space telescopes and observatories stationed at L1, such as the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) and the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE), provide continuous and unobstructed views of the Sun. These observations are essential for studying solar activity, solar flares, and their potential impacts on Earth’s technological infrastructure.
Earth Monitoring and Communications :-
Lagrange points can be used for Earth-focused applications as well:
Earth Observation Satellites :- Placing Earth-observing satellites at Lagrange points allows them to maintain a fixed position relative to Earth, making them ideal for monitoring weather patterns, natural disasters, and environmental changes.
Communication Relay Stations :- Lagrange points, specifically L4 and L5, can serve as relay stations for communication satellites. These points can help extend the coverage and capacity of satellite communication networks.
Future Space Colonization :-
In the long-term vision of space exploration, Lagrange points hold potential significance for human colonization beyond Earth:
Stable Habitation :- The gravitational balance at Lagrange points reduces the need for constant propulsion to maintain orbit, making these points attractive for the construction of space habitats. These habitats could support scientific research, mining operations, and serve as waystations for deep-space missions.
Planetary Defense :- Lagrange points, particularly L1 and L2, can be strategic locations for early detection and deflection of near-Earth objects (NEOs) such as asteroids and comets. By monitoring the space near these points, scientists and space agencies can develop strategies to mitigate potential impact threats to Earth. In summary, Lagrange points offer a wide range of applications in space exploration, from providing stable orbits for satellites and observatories to facilitating efficient interplanetary travel and supporting future space colonization efforts. These points serve as valuable assets in our quest to understand the cosmos and expand our presence in space.
The Exploration Continues :-
As humanity’s interest in space exploration and astronomy grows, Lagrange points will continue to play a pivotal role. These gravitational sweet spots offer unique advantages for scientific research, space missions, and the development of future space technologies. In conclusion, Lagrange points are indeed gravitational balance points in space, where celestial forces create a delicate equilibrium. These cosmic locations have opened up new possibilities for our understanding of the universe and our ability to explore it. As we look to the stars and dream of new horizons, Lagrange points will remain a crucial chapter in our cosmic journey.